Submit
Submit feedback
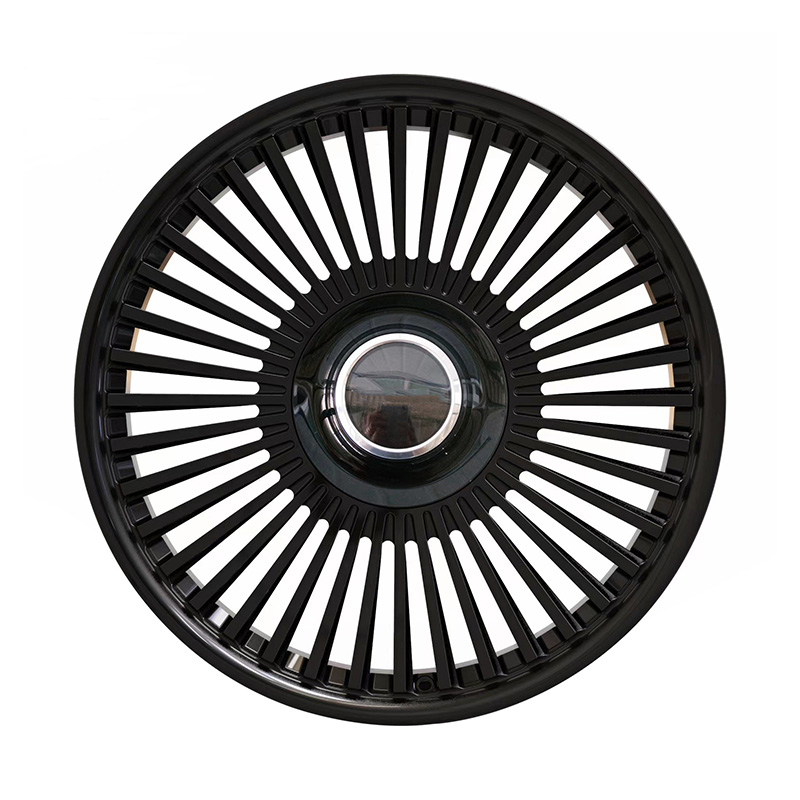
Understanding the Physical Properties of Deep Lip Concave Wheels
2024-11-08
Deep lip concave wheels are a striking and functional design feature in automotive customization, offering both aesthetic appeal and performance advantages. The unique physical properties of these wheels stem from their design and material choices, which influence their strength, handling, and weight distribution.
At the core of a deep lip concave wheel is the shape, characterized by a deep inward curve at the center, often referred to as the “concave” portion. This design increases the wheel's strength by redistributing the forces applied during driving. The deeper the concave, the more pronounced the curve, bringing about a greater concentration of strength around the wheel’s outer edge. This can enhance the performance of a vehicle by providing better handling, as the wheel is more resistant to deformation under high pressure or sharp turns.
In addition to strength, the deep lip concave design allows for greater weight distribution, which can lower the overall rotational mass. Lower rotational mass is beneficial because it reduces the load on the vehicle’s suspension, thus improving overall driving dynamics and fuel efficiency. This is particularly advantageous in high-performance vehicles or those used for racing, where every gram counts.
The physical structure of deep lip concave wheels also influences airflow. The unique shape, with a larger surface area at the edge and a recessed center, can improve brake cooling. Better air circulation around the brakes can reduce the risk of overheating, enhancing the vehicle's stopping power and safety.
The material used in these wheels, often a high-grade alloy or forged aluminum, adds to their rigidity and resistance to corrosion while keeping them relatively lightweight. These materials contribute to a balance between durability and performance, making deep lip concave wheels a popular choice for automotive enthusiasts.
The use of aluminum alloys in car concave deep dish wheels is a key element in their performance and popularity. Aluminum alloys are preferred over other materials for their favorable combination of strength, weight, and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for wheels that need to withstand the rigors of daily driving or high-performance applications.
Aluminum, as a base metal, is relatively lightweight compared to steel, making it an choice for reducing the overall weight of a vehicle. By incorporating alloying elements like silicon, magnesium, and copper, aluminum can be enhanced to provide a stronger, more durable wheel without adding excessive weight. This is especially important for concave deep dish wheels, where the design aims to maintain structural integrity while managing the complex forces exerted on the wheel during acceleration, braking, and cornering.
Magnesium, a common addition to aluminum alloys, improves the material's strength-to-weight ratio. Magnesium alloys allow manufacturers to produce lighter wheels with strength and performance characteristics. In high-performance and racing applications, where every ounce counts, these magnesium-aluminum alloys help to improve overall vehicle performance by reducing unsprung weight, which in turn boosts handling and acceleration.
Silicon is another critical element in many aluminum alloys used for concave wheels. It improves the material's castability and fluidity during the manufacturing process, making it easier to form complex shapes, such as the deep dish concave design while maintaining uniform strength across the wheel. The alloy's improved resistance to corrosion is especially important for wheels exposed to the elements, where road salt, rain, and UV radiation can cause premature wear and degradation.
recommend products
-
Zhenlun Multi Spokes Split Monoblock Forged Wheels Bronze With Silver Lip Edge
-
Zhenlun Matt Black With Red Lip Monoblock Forged Wheels
-
Zhenlun Gloss Black Monoblock Forged Wheels Gloss Black For Sports Car
-
Zhenlun Monoblock Forged Wheels Lightgrey With Machined Face
-
Zhenlun Monoblock Forged Wheels Gloss Black Dense Multi Spoke

 0
0