Submit
Submit feedback
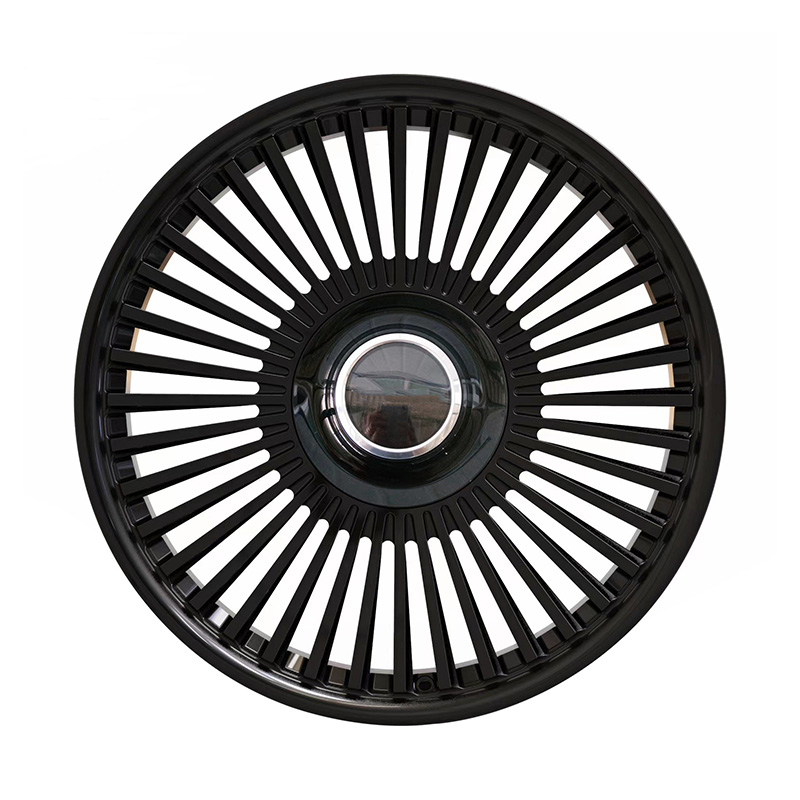
Innovative Forged Wheels Set New Standards for Performance and Aesthetics
2024-06-27
Monoblock Forged Wheels has emerged as the epitome of engineering excellence and design innovation in a world where every detail counts. These wheels are not just another accessory; they are a testament to the relentless pursuit of perfection in the automotive sector.
The heart of Monoblock Forged Wheels lies in their manufacturing process. Unlike traditional cast wheels, which are made by pouring molten metal into a mold, monoblock forged wheels are crafted through a process of forging. This involves heating a single piece of high-grade aluminum alloy to a precise temperature and then hammering it into shape using hydraulic presses. The result is a wheel that is up to 30% lighter and significantly stronger than its cast counterparts.
Advantages Of Traditional Wheels
The benefits of monoblock forged wheels are manifold. Here are some of the key advantages:
1. Enhanced Strength and Durability: The forging process creates a denser molecular structure, making the wheels more resistant to impact and wear.
2. Reduced Weight: Lighter wheels improve the vehicle's handling and acceleration, as well as reduce unsprung weight, to better ride quality and fuel efficiency.
3. Customization: Monoblock forged wheels can be tailored to fit a wide range of vehicles, offering a level of customization that is unmatched by traditional wheels.
4. Aesthetic Appeal: With a sleek design and the option for various finishes, these wheels add a touch of sophistication and style to any vehicle.
The automotive industry has responded positively to the introduction of monoblock forged wheels. Car manufacturers and aftermarket suppliers alike recognize this technology's potential to enhance vehicle performance and appearance.
Monoblock wheels, also known as one-piece wheels, are made from a single piece of material, typically forged or cast aluminum, resulting in a solid and uniform structure. Unlike multi-piece wheels, which are composed of separate components that are joined together, monoblock wheels offer strength and fewer points of potential failure. There are various types of monoblock wheels, each offering specific advantages and characteristics suited for different applications.
Cast monoblock wheels are made from a single aluminum alloy that is melted and poured into a mold. The casting process is relatively cost-effective and allows for intricate designs and shapes. However, cast wheels are generally not as strong as forged wheels, and they can be more susceptible to damage under stress or harsh conditions. Despite this, they are widely used in everyday vehicles because of their affordability and availability in a variety of designs.
Forged monoblock wheels are made by taking a solid billet of aluminum and shaping it under high pressure using heat and mechanical force. The forging process results in a denser and stronger material compared to casting. Forged monoblock wheels are highly durable and lightweight, making them a preferred choice for high-performance vehicles, racing applications, and off-roading. They offer improved strength-to-weight ratios, making them capable of withstanding higher stresses and impacts.
4x100 painting cast aluminum wheels are commonly found on compact and subcompact vehicles, particularly those used for daily commuting and city driving. While cast aluminum wheels offer several benefits, including relatively low weight and good corrosion resistance, they are not immune to defects that can arise during manufacturing or due to improper use. Here, we will explore some common defects that can occur in 4x100 painting cast aluminum wheels.
One of the common defects seen in 4x100 painting cast aluminum wheels is paint chipping or scratching. The paint applied to these wheels serves both an aesthetic and protective function, preventing corrosion and giving the wheels a polished, clean look. However, the paint can be susceptible to chipping, especially if the wheel experiences physical impacts, such as hitting curbs or rough road surfaces. Over time, this can unsightly marks and expose the metal beneath, increasing the likelihood of corrosion.
Although cast aluminum is relatively lightweight and durable, it is more prone to cracking under stress compared to forged wheels. The casting process can sometimes result in uneven material distribution or air pockets within the wheel, weakening the overall structure. These imperfections can cracks, which may not be immediately visible but can compromise the safety of the wheel over time. Cracks can develop from impacts, such as hitting potholes or curbs, and in cases, they can wheel failure.
recommend products
-
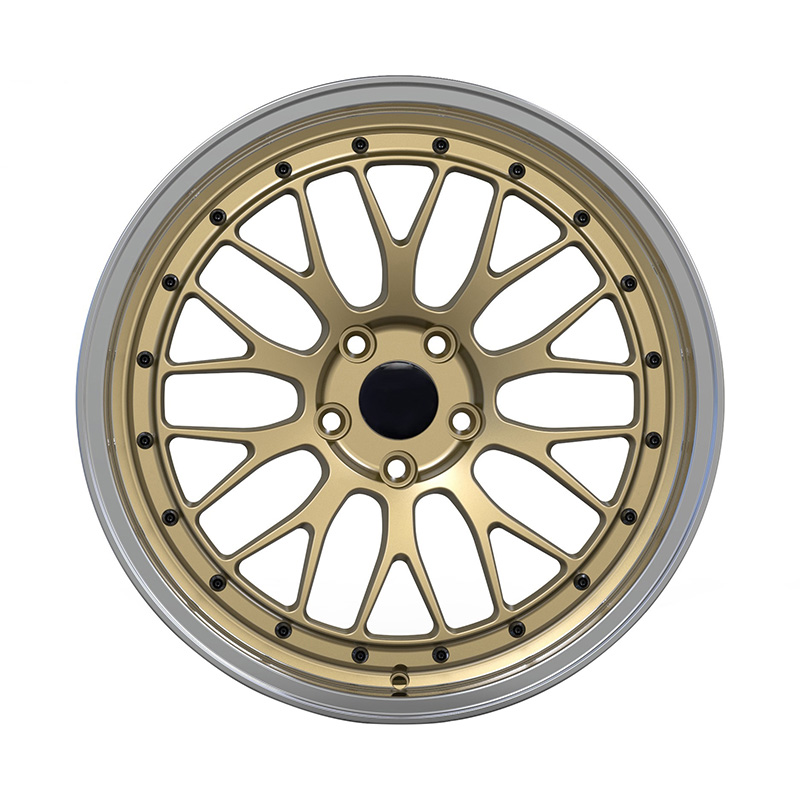
Zhenlun Multi Spokes Split Monoblock Forged Wheels Bronze With Silver Lip Edge
-
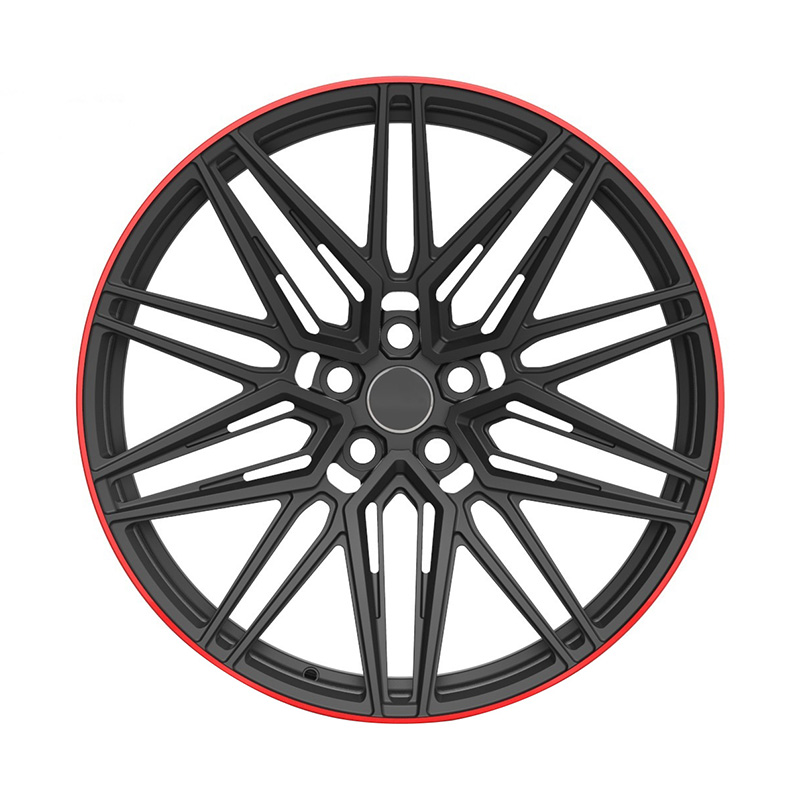
Zhenlun Matt Black With Red Lip Monoblock Forged Wheels
-
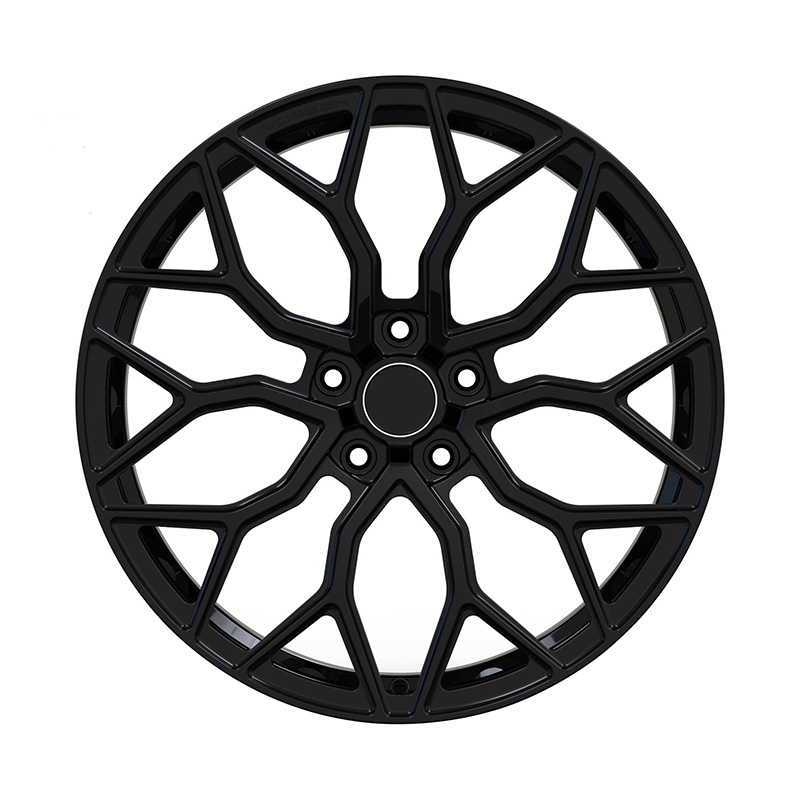
Zhenlun Gloss Black Monoblock Forged Wheels Gloss Black For Sports Car
-
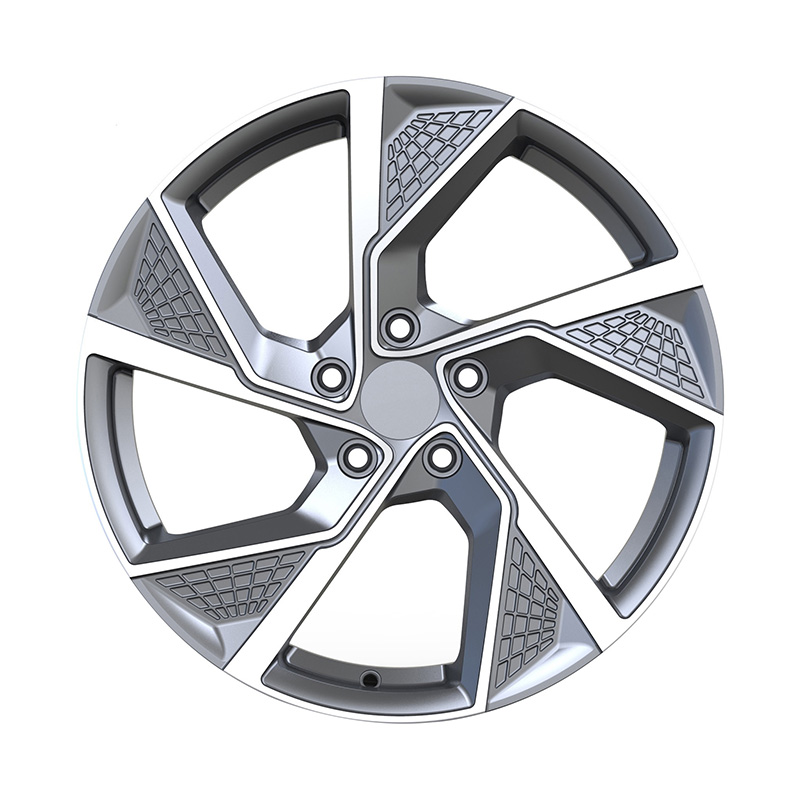
Zhenlun Monoblock Forged Wheels Lightgrey With Machined Face
-
Zhenlun Monoblock Forged Wheels Gloss Black Dense Multi Spoke

 0
0